A use case diagram contains four components.
- The boundary, which defines the system of interest in relation to the world around it.
- The actors, usually individuals involved with the system defined according to their roles.
- The use cases, which are the specific roles played by the actors within and around the system.
- The relationships between and among the actors and the use cases.
We can use the following elements in use case diagrams :
Actor : An actor represents a role that an outsider takes on when interacting with the business system. For instance, an actor can be a customer, a business partner, a supplier, or another business system.
Association : An association is the relationship between an actor and a business use case. It indicates that an actor can use a certain functionality of the business system - the business use case.
Use Case : A business use case describes the interaction between an actor and a business system, meaning it describes the functionality of the business system.
Include : The include relationship is a relationship between two business use cases that signifies that the business use case on the side to which the arrow points is included in the use case on the other side of the arrow. This means that for one functionality that the business system provides, another functionality of the business system is accessed.
Generalization : A generalization relationship is also a
parent-child relationship between use cases. The child use case in the
generalization relationship has the underlying business process meaning, but is
an enhancement of the parent use case. In a use case diagram, generalization is
shown as a directed arrow with a triangle arrowhead. The child use case is
connected at the base of the arrow. The tip of the arrow is connected to the
parent use case.
Extends : An extends shows the relationships between
use cases. Relationship between use case A and use case B indicates that an
instance of use case B may include (subject to specified in the extension) the
behavior specified by A. An 'extends' relationship between use cases is
depicted with a directed arrow having a dotted shaft. The tip of arrowhead
points to the parent use case and the child use case is connected at the base
of the arrow. For example, validating the user for a system. A invalid password
is extension of validating password use case.
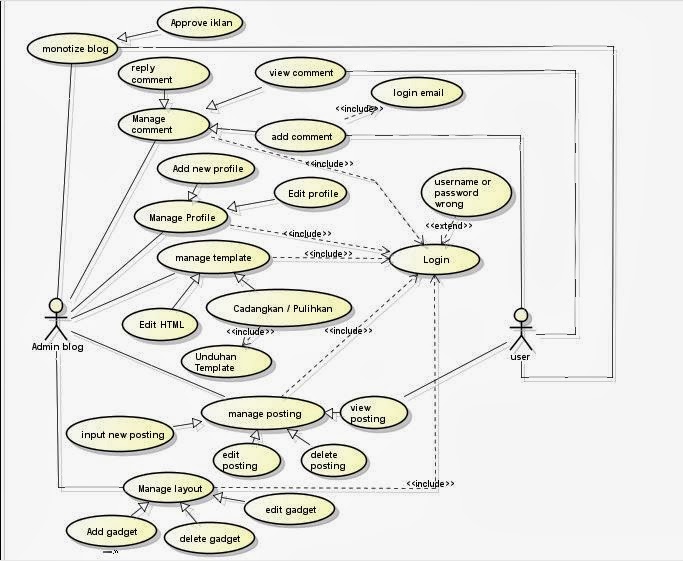
Here’s simple example of use case diagram about
blog system :
Monetize
blog
Here you can add ads to your blog. When you
sign up with one of these services, you’re given code to add to your site that
will link to whatever content or services those companies are currently
promoting. Other sponsored ads come from individual companies and promote only
that company and its products or services. After that you can put these ads in
the section you want.
Manage comment
You can see the existing comments and can
reply a comment from the visitors. Visitors can also see the comments on the
blog, as well as be able give a comment only after login using their own email
visitors.
Manage profile
You can add a new profile on the blog if you
have already registered in the email. If you are logged into your emails, then
you have to create a new blog. Here you can also edit your profile.
Manage template
Here you can change the background by using a
basic template and then customize the background, layout, colors, fonts, etc. But
first you have to download a template for a blog on the internet.
Manage
posting
You can add and publish your new post, and can
also edit and delete existing blog posts. You can see your own post by clicking
on the blog look. Visitors can also see and visit our blog for free, whenever
and wherever.
Manage
layout
The manage layout you can add, delete and edit
gadget in your blog. or you can click and drag to rearrange the gadgets.





1 komentar:
Nice Post!
UML Diagram Help
Posting Komentar